Proper installation of architectural hinges on commercial building doors involves selecting the right hinges, ensuring correct placement and spacing, aligning the hinges accurately, pre-drilling holes, and using appropriate screws. Additionally, consider the door's weight, usage frequency, and compliance with fire safety regulations. Regular maintenance and inspection are essential to ensure long-term performance and durability. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that the doors in commercial buildings operate smoothly and reliably.
Here are some guidelines and considerations to follow:
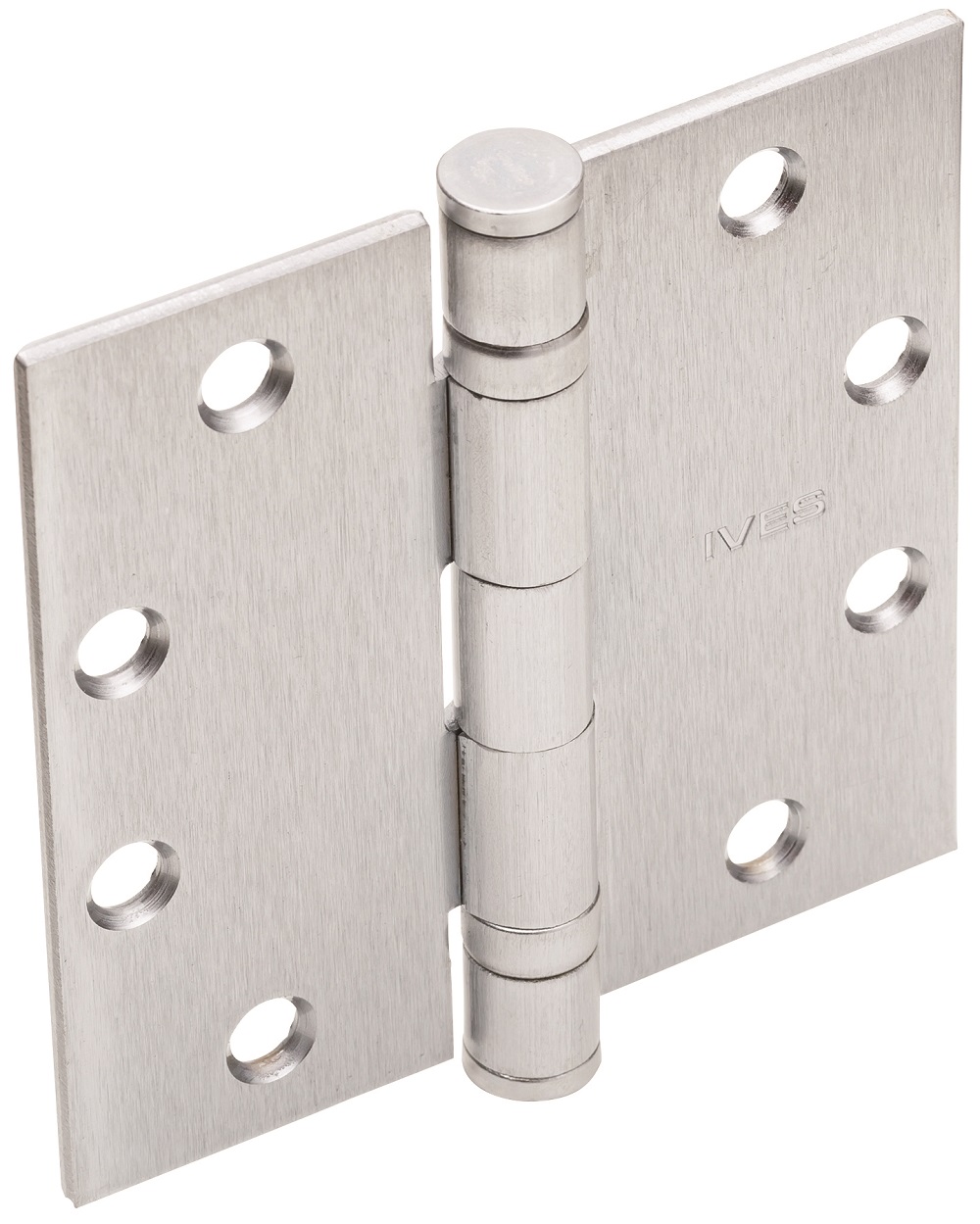
1. Selecting the Right Hinges
Hinge Type: Choose the appropriate hinge type for the door's weight, usage frequency, and application (e.g., ball bearing hinges for high-traffic areas).
Material: Ensure the hinge material is suitable for the environment (e.g., stainless steel for corrosive environments).
Size: Select the correct hinge size based on the door dimensions and weight.
2. Number of Hinges
Standard Doors: Typically, three hinges are used for standard-sized doors. For heavier or taller doors, additional hinges may be required.
Heavy Doors: For doors over 200 pounds or taller than 7 feet, consider using four or more hinges to distribute the weight evenly.
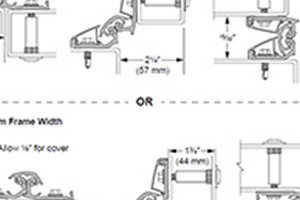
3. Placement and Spacing
Top Hinge: Install the top hinge 5-7 inches from the top of the door.
Bottom Hinge: Place the bottom hinge 10-12 inches from the bottom of the door.
Middle Hinges: Space additional hinges evenly between the top and bottom hinges.
4. Proper Alignment
Vertical Alignment: Ensure the hinges are vertically aligned to prevent the door from binding or sagging.
Horizontal Alignment: The hinge leaves should be flush with the door and frame surfaces for a smooth operation.
5. Pre-Drilling and Screwing
Pre-Drilling: Pre-drill holes for screws to prevent splitting the wood or damaging the door material.
Screw Length: Use screws of sufficient length to penetrate the door frame and provide a secure hold. For heavy doors, consider using longer screws.
6. Hinge Mortising
Mortise Depth: The depth of the mortise should match the thickness of the hinge leaf to ensure a flush fit.
Chisel Work: Use a sharp chisel to create clean and precise mortises for the hinges.
7. Load-Bearing Capacity
Weight Distribution: Ensure that the hinges can support the door's weight without causing sagging or misalignment over time.
Heavy-Duty Hinges: For particularly heavy doors, use heavy-duty hinges designed to handle greater loads.
8. Fire-Rated Doors
Compliance: Use hinges that comply with fire safety regulations for fire-rated doors.
Ball Bearing Hinges: For fire-rated openings, ball bearing or concealed bearing hinges are usually recommended to ensure smooth operation under stress.
9. Door Closers and Other Hardware
Compatibility: Ensure that the hinges are compatible with other door hardware, such as door closers, locks, and panic bars.
Load Sharing: When door closers are used, hinges with ball bearings or anti-friction bearings are recommended to handle the additional load.
10. Regular Maintenance
Inspection: Regularly inspect hinges for wear and tear, ensuring that screws are tight and the door operates smoothly.
Lubrication: Periodically lubricate the hinges to prevent squeaking and ensure smooth operation.
Architectural Hinges Template PDF















-871x291.jpg)
%20-871x291.jpg)